
Functional glycosylation of human podoplanin: glycan structure of platelet aggregation-inducing factor.FEBS Lett. 2007 Jan 23;581(2):331-336.
(Reference)
Adachi Y et al., Lymphatic vessel density in pulmonary adenocarcinoma immunohistochemically evaluated with anti-podoplanin or anti-D2-40 antibody is correlated with lymphatic invasion or lymph node metastases. Pathol Int. 2007 Apr;57(4):171-7.
(PubMed)<注>anti-D2-40 antibodyとなっているが、D2-40は抗体の名前であり、抗原名ではない。抗原はpodoplaninである。
D2-40と他の抗podoplanin抗体は同じ抗原(podoplanin)を認識しており、単に抗体の反応性が違うだけである。
Adenoviral Transduction of MRP-1/CD9 and KAI1/CD82 Inhibits Lymph Node Metastasis in Orthotopic Lung Cancer Model. Cancer Res. 2007 Feb 15;67(4):1744-1749
(PubMed)MRP-1/CD9やKAI1/CD82はテトラスパニンである。ともにリンパ節転移を抑制した。
以前にも以下のような報告がある。(同様の報告が他にもいろいろある。)
Motility-related protein (MRP-1/CD9) and KAI1/CD82 expression inversely correlate with lymph node metastasis in oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Br J Cancer. 1999 Mar;79 (7-8) :1168-73.
Mohammed RA. et al., Prognostic significance of vascular endothelial cell growth factors -A, -C and -D in breast cancer and their relationship with angio- and lymphangiogenesis.
(PubMed)
Hinterberger M., et al., D2-40 and calretinin-a tissue microarray analysis of 341 malignant mesotheliomas with emphasis on sarcomatoid differentiation. Mod Pathol. 2007 Feb;20(2):248-55.
(PubMed)
Hantusch et al., Sp1/Sp3 and DNA-methylation contribute to basal transcriptional activation of human podoplanin in MG63 versus Saos-2 osteoblastic cells. BMC Mol Biol. 2007 Mar 7;8(1):20 [Epub ahead of print]
(PubMed)
骨肉腫細胞のMG63にはポドプラニンが高発現している。この転写制御について調べたところ、Sp1とSp3という転写因子が関わっていることがわかった。骨肉腫細胞のSaos-2にはこれらの転写因子が不足しており、ポドプラニンの発現が低いことがわかった。また、メチル化もポドプラニンの転写調節に関わっていることもわかった。
これまで、リンパ管内皮細胞においては、リンパ管特異的は制御因子であるProx-1がポドプラニンの転写調節に関わっていることが報告されている。また、内在性のIL-3がリンパ管内皮細胞におけるポドプラニンの発現の制御に重要な役割を果たしていることも知られている。
またラットのI型肺胞上皮細胞については、Sp1やTGT3/HNF-3という転写因子がポドプラニンの転写制御を行っているようである。
Nakayama et al., Significance of lymphangiogenesis as assessed by immunohistochemistry for podoplanin in patients with esophageal carcinoma. Anticancer Res. 2007 Jan-Feb;27(1B):619-25.
(PubMed)
食道の扁平上皮癌症例について、ポドプラニンを用いてリンパ管新生の量(LMVD)を測定したところ、リンパ管新生の量とリンパ節転移や患者予後に相関関係が見られた。
木村 仁、加藤 広行、猪瀬 崇徳、宗田 真、中島 政信、深井 康幸、宮崎 達也、増田 典弘、萬田 緑平、福地 稔、尾嶋 仁、塚田 勝彦、桑野 博行
食道扁平上皮癌におけるAggrus(Podoplanin/T1α)の発現の意義
日本外科学会雑誌 Journal of Japan Surgical Society Vol.107, No.臨時増刊号_2(20060305) p.678
(CiNii)

今年はAACR(アメリカ癌学会)が100周年ということで、記念式典も行われた。ポドプラニンに関しては、演題が3つ出され、ポドプラニンの臨床的意義に関するミニシンポジュウムもあった。今後、臨床応用が期待できる。

(AACR 2007)
・Podoplanin expression is an independent predictor of survival in malignant gliomas.
Erik P. Sulman, Christopher E. Pelloski, J. Matthew McDonald, Clarissa De La Cruz, Lihong Long, Sonya C. Popoff, Susan L. McGovern, Howard Colman, Kenneth D. Aldape.
The University of Texas M. D. Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, TX
膠芽腫(glioblastoma;GBM)において、ポドプラニンが発現していると、患者の予後が悪くなることがわかり、ポドプラニンがGBMにおいても予後不良因子であることが明らかになった。これまでは、頭頸部扁平上皮癌(HNSCC)において、ポドプラニンが予後不良因子であることがわかっていた(MACCのDr. Maoラボ)が、これが2つ目の報告となる。GBMにおけるポドプラニンの発現解析は、MishimaらがANPに報告しており、astrocytic tumorのmalignant progressionに関係していることはわかっていた。
Despite aggressive clinical care, glioblastoma (GBM) is a near uniformly fatal disease with median survival of 10 to 12 months. Few molecular markers exist that are prognostic for overall survival. Data from multiple expression profiling experiments suggested that the mucin-type transmembrane glycoprotein podoplanin may be a significant marker of survival. We sought to validate this finding in an independent cohort of GBM patients. Cases of GBM (WHO grade IV) or low and intermediate grade astrocytoma (WHO grade II and III) who underwent surgical resection from 11/1985 to 6/2005 with available medical records and archival formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded (FFPE) tumor tissue were selected for this study. Podoplanin expression was detected by immunohistochemical (IHC) staining and scored as negative, intermediate, or high expression. Radiation response was previously determined in patients without a gross-total resection by evaluation of magnetic resonance imaging. Quantitative real-time PCR (QPCR) of PDPN cDNA was performed following reverse transcription of total RNA derived from FFPE tissue. A total of 113 GBMs were initially examined for podoplanin expression by IHC using the D2-40 antibody. Median survival in the podoplanin expressing group was 60 wks vs. 148 wks in the non-expressing group (p=0.008, log-rank test). This result was validated using an independent set of 95 GBMs with a 2 year survival of 52% vs. 10% (p=0.017). Median and 2-year survival among all GBMs (median follow-up of 55 weeks) for podoplanin expression vs. non-expression was 54 wks vs. 148 wks and 15% vs. 56%, respectively (p<0.0001). Podoplanin expression was an independent predictor of survival after adjustment for age or extent of surgical resection (HR 2.3, 95% CI 1.3-4.3, Cox multivariate regression). The presence of podoplanin expression was also associated with poorer radiation response among the 72 patients who underwent sub-total tumor resection. IHC results were validated using QPCR of cDNA derived from 74 GBMs. In addition, we examined podoplanin expression in a panel of 93 WHO grade II and III astrocytomas and observed a correlation to survival. The estimated 5-year survival for negative-, intermediate- and high-podoplanin levels was 82%, 65%, and 20%, respectively (p < 0.001). Podoplanin level was independent of age and grade among the astrocytomas in predicting overall survival (HR 3.3, 95% CI 1.4-10.0). The results indicate that podoplanin is a novel prognostic marker of survival in low-grade and malignant astrocytomas. It correlates to radiation response and is independent of powerful clinical prognostic markers such as age and extent of surgical resection. Further analysis of its functional role in tumor progression is indicated.
・Podoplanin expression is a novel marker of oral cancer risk in patients with oral premalignancy.
Li Mao, Hidetoshi Kawaguchi, Hening Ren, Zouming Chu, You-Hong Fan, Lei Feng, Jack Lee, Adel El-Naggar, Edward Kim, Waun Ki Hong, Scott Lippman.
UT M.D. Anderson Cancer Ctr., Houston, TX.
昨年の頭頸部扁平上皮癌における解析に引き続き、ポドプラニンが白斑症から口腔癌に進展するrisk factorになることを報告した。
Background: Oral leukoplakia (OL) is a heterogeneous oral lesion with an increases oral cancer risk. However, clinical assessment is not sufficient to distinguish premalignancies vs. benign conditions among OL. We recently reported that podoplanin, a lymphatic endothelial factor, is highly expressed in oral cancer and some oral premalignancies. The purpose of this study is to evaluate podoplanin as a biomarker in assessing oral cancer risk in patients with OL. Methods: Podoplanin expression was determined in 150 OL patients with long-term follow-up using immunohistochemistry. Associations between the protein expression patterns and clinicopathologic parameters including cancer development during the follow-up were analyzed. Results: One hundred and eight (72%) of the 150 OL expressed podoplanin including 56 (37%) with expression extended above basal layer (podoplanin positive cases). Podoplanin positive was more frequent in older patients (P = 0.016), females (P = 0.020), and dysplastic histology (P = 0.020). Patients whose OL showed podoplanin positive developed significantly more invasive oral cancers than those whose OL were podoplanin negative (P = 0.0002). At 5 years, 92% (95% confidence interval [CI] = 0.86, 0.98) podoplanin negative patients were oral cancer free compared to only 63% (CI = 0.51, 0.77) podoplanin positive patients did so. In the multivariate analysis, podoplanin positive was the only independent factor for the oral cancer development (Hazard Ratio, 3.09; CI = 1.53, 6.24; P = 0.0017). Conclusions: Podoplanin is frequently expressed in OL and may serve as a powerful biomarker to predict risk of oral cancer development for patients with OL.
Shu W, Lu MM, Zhang Y, Tucker PW, Zhou D, Morrisey EE. Foxp2 and Foxp1 cooperatively regulate lung and esophagus development. Development. 2007 Apr 11; [Epub ahead of print]
(PubMed)
・ポドプラニンの転写制御については、骨肉腫細胞のMG63においてはSp1とSp3という転写因子が、リンパ管内皮細胞においてはリンパ管特異的制御因子であるProx-1が、またラットのI型肺胞上皮細胞については、Sp1やTGT3/HNF-3という転写因子が関わっているという報告があった。
・今回、Foxp1/2という転写因子が、マウスのポドプラニンの転写制御をしていることがわかった。Foxp1/2はポドプラニンの発現を負に制御している。Foxp1/2のノックアウトマウスにおいては、I型肺胞上皮細胞のポドプラニン(T1 alpha)の発現量が上昇する。このマウスは生後約3週間で、肺の発達障害により致死となる。肺胞におけるポドプラニンの過剰発現により、hyperoxic injuryによる致死率が上がるという報告もあり、Foxp1/2による負の制御が肺の発達に重要なようである。
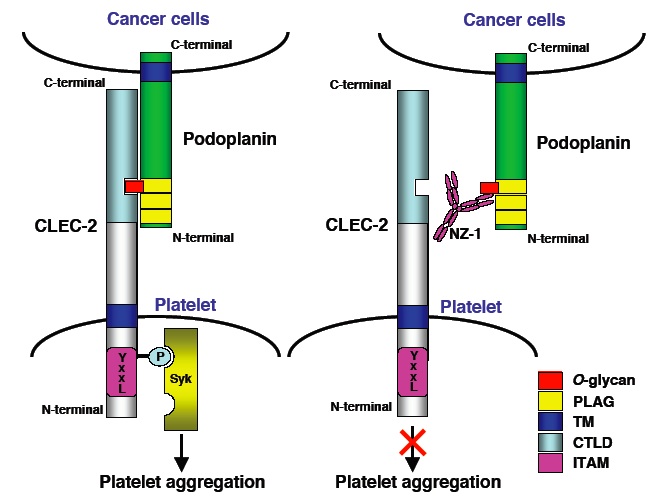
ポドプラニンのレセプターがCLEC-2であることが判明した。
(PubMed)
Suzuki-Inoue K, Kato Y, Inoue O, Kaneko MK, Mishima K, Yatomi Y, Narimatsu H, Ozaki Y.
Involvement of the snake toxin receptor CLEC-2 in podoplanin-mediated platelet activation by cancer cells.
J Biol Chem. 2007 Jul 6; [Epub ahead of print]
第16回日本がん転移学会において、<血小板凝集因子Aggrus/podoplaninの分子生物学的解析>が日本がん転移学会研究奨励賞を受賞。
・Yukinari Kato, Mika Kato Kaneko, Akiko Kunita, Hiromi Ito, Akihiko Kameyama, Satoshi Ogasawara, Nana Matsuura, Yasushi Hasegawa, Katsue Suzuki-Inoue, Osamu Inoue, Yukio Ozaki and Hisashi Narimatsu
Molecular analysis of pathophysiological binding of the platelet aggregation-inducing factor podoplanin to the C-type lectin-like receptor CLEC-2.
Cancer Science, in press
(Reference)
・「井上准教授らが血小板凝集と癌の転移に関する研究成果を発表」(山梨大学)
Suzuki-Inoue et al., Involvement of the snake toxin receptor CLEC-2 in podoplanin-mediated platelet activation by cancer cells. J Biol Chem. 282(36):25993-26001, 2007が、JBCの<Paper of the week>に選ばれた。(JBC, Paper of the week)
・Yu H, Pinkus GS, Hornick JL. Diffuse membranous immunoreactivity for podoplanin (d2-40) distinguishes primary and metastatic seminomas from other germ cell tumors and metastatic neoplasms. Am J Clin Pathol. 2007 Nov;128(5):767-75.
(PubMed)
・Yu H, Gibson JA, Pinkus GS, Hornick JL. Podoplanin (d2-40) is a novel marker for follicular dendritic cell tumors. Am J Clin Pathol. 2007 Nov;128(5):776-82.
(PubMed)
・Yukinari Kato, Mika Kato Kaneko, Akiko Kunita, Hiromi Ito, Akihiko Kameyama, Satoshi Ogasawara, Nana Matsuura, Yasushi Hasegawa, Katsue Suzuki-Inoue, Osamu Inoue, Yukio Ozaki and Hisashi Narimatsu
Molecular analysis of pathophysiological binding of the platelet aggregation-inducing factor podoplanin to the C-type lectin-like receptor CLEC-2.
Cancer Science, 2007 Oct 18; [Epub ahead of print]
(PubMed)
・第27回日本分子腫瘍マーカー研究会において、<ヒト腫瘍におけるPodoplaninの糖鎖構造解析および免疫組織学的解析>が学術奨励賞を受賞。(日本分子腫瘍マーカー研究会)
・「がん増殖 血小板の作用を山梨大研究班が解明」(山梨日日新聞社 9月11日掲載)
・特異性の高いリンパ管内皮細胞マーカー抗体NZ-1(コスモバイオニュース No.64(Sep 2007))
・本ホームページのhit数が1万を突破。
(1万hit)
・GISTにおけるポドプラニンの発現。
(GIST)
・Fujii T, Zen Y, Sato Y, Sasaki M, Enomae M, Minato H, Masuda S, Uehara T, Katsuyama T, Nakanuma Y. Podoplanin is a useful diagnostic marker for epithelioid hemangioendothelioma of the liver. Mod Pathol. 2007 Dec 14; [Epub ahead of print] PMID: 18084256 [PubMed - as supplied by publisher]
(PubMed)
肝腫瘍におけるポドプラニン発現の詳細な解析はこの論文が初めてである。肝腫瘍の中で、epithelioid hemangioendotheliomaのみに、ポドプラニンが特異的に発現している。抗体はD2-40を使っている。以前、肝細胞癌(HCC)にもポドプラニンが発現しているという論文(Kono T., et al, Int J Oncol. 2007)があったが、それがnon-specificな反応を報告していたことが明らかとなった。(同様に、NZ-1抗体でもHCCは染色されない。)
・平成19年度井上研究奨励賞を受賞
<血小板凝集因子Aggrusの分子生物学的解析とその臨床応用>(井上研究奨励賞)